KEY TAKEAWAYS:
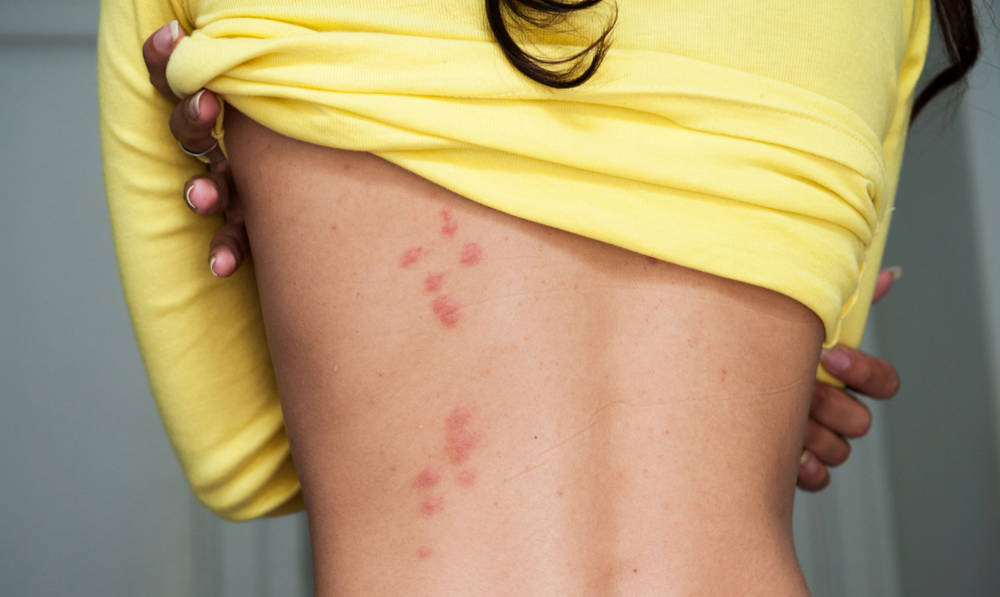
Appearance and Patterns: Bed bug bites are small, red, swollen spots that appear in clusters or lines, often with a central blister.
Common Locations: Bites are typically on exposed skin like arms, shoulders, neck, face, legs, and feet, occurring mostly at night.
Variable Reactions: Reactions range from mild itching to severe allergic responses with intense itching and blisters.
Differentiation: Bed bug bites differ from mosquito (isolated), flea (legs and ankles with a red halo), and spider bites (single, large, inflamed).
Confirmation and Prevention: Inspect bedding for bugs and stains, use bed bug-proof covers, vacuum regularly, and be cautious with second-hand furniture.
While they don’t transmit diseases, recognizing bed bug bites early can help you address the problem promptly.
Here’s how to identify bed bug bites and distinguish them from other insect bites.
Recognizing Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites typically manifest as small, red, and swollen spots. They often appear in clusters or lines, reflecting the bed bug’s feeding pattern. The bites are usually red, slightly swollen, and may develop into raised welts.
In some cases, a small blister can form in the center of the bite. Unlike mosquito bites that are generally isolated, bed bug bites are often found in clusters on exposed skin areas like arms, shoulders, neck, face, legs, and feet.
Timing and Reaction
Bed bug bites occur primarily at night when you are asleep. The itching and swelling from the bites may become noticeable immediately, but sometimes it can take several days for the symptoms to develop. People’s reactions to bed bug bites can vary widely.
While some experience intense itching and swelling, others may have a minimal or delayed reaction. In rare cases, severe allergic reactions can occur, resulting in intense itching, blisters, or hives.
Differentiating Bed Bug Bites from Other Insect Bites
Bed bug bites can resemble bites from mosquitoes, fleas, or spiders, making identification challenging.
Mosquito bites are usually isolated and can appear anywhere on the body, whereas bed bug bites often appear in clusters or lines on exposed skin.
Flea bites are commonly found on the legs and ankles and may have a red halo around the bite, unlike bed bug bites, which are more likely to be on the upper body in a linear pattern.
Spider bites typically result in a single, large, inflamed bite, while bed bug bites are multiple and smaller.
Confirming a Bed Bug Infestation
If you suspect bed bug bites, it’s crucial to confirm their presence. Start by inspecting your bedding and furniture.
Bed bugs are small, reddish-brown, and about the size of an apple seed. Check the seams and tags of mattresses and box springs for signs of bugs, rusty stains, or tiny dark spots of excrement.
Using bed bug monitors like the Clearview Bed Bug Monitor can also help in detecting bed bugs. If you find evidence of an infestation or continue to get bitten, consulting a pest control professional is advisable.
Preventing and Treating Bed Bug Bites
To prevent bed bug bites, encase mattresses and box springs in bed bug-proof covers, vacuum regularly, and keep your home clutter-free. Be cautious with second-hand furniture, thoroughly inspecting it before bringing it home.
If bitten, wash the affected area with soap and water. Applying anti-itch cream or taking antihistamines can help reduce itching. Avoid scratching the bites to prevent infection.
Identifying bed bug bites involves observing specific patterns and characteristics and distinguishing them from other insect bites. Confirming the presence of bed bugs through careful inspection and using detection tools is essential for taking prompt action.
Proper identification and swift measures can help manage and eliminate bed bugs, ensuring a more comfortable and restful living environment.
If you are uncertain, seeking professional assistance is the best course of action.